To connect to a MySQL database using Python, you can use the `mysql.connector` module. Here's a stepbystep guide:
1. Install the mysqlconnectorpython package: If you haven't already installed the `mysqlconnectorpython` package, you can do so using pip: ``` pip install mysqlconnectorpython ```
2. Establish a connection: Use the `connect` method from the `mysql.connector` module to establish a connection to the MySQL database. You'll need to provide the following parameters: `host`: The hostname or IP address of the MySQL server. `user`: The username for the MySQL database. `password`: The password for the MySQL database. `database`: The name of the database you want to connect to.
3. Create a cursor object: After establishing the connection, create a cursor object using the `cursor` method. The cursor object is used to execute SQL queries and fetch data from the database.
4. Execute a query: Use the `execute` method of the cursor object to execute an SQL query. For example, to select all rows from a table named `your_table`, you can use: ```python cursor.execute ```
5. Fetch data: Use the `fetchall` method to fetch all the rows returned by the query. This method returns a list of tuples, where each tuple represents a row in the table.
6. Close the cursor and connection: It's important to close the cursor and connection when you're done working with the database to free up resources. Use the `close` method to close the cursor and connection objects.
Here's a complete example that demonstrates how to connect to a MySQL database, execute a query, and fetch the results:
```pythonimport mysql.connector
Establish a connection to the MySQL databaseconn = mysql.connector.connect
Create a cursor object using the cursor methodcursor = conn.cursor
Execute a querycursor.execute
Fetch all the rows in a list of lists.results = cursor.fetchallfor row in results: print
Close the cursor and connectioncursor.closeconn.close```
Make sure to replace `yourusername`, `yourpassword`, `yourdatabase`, and `your_table` with your actual MySQL credentials and table name.
Python3衔接MySQL数据库的具体教程
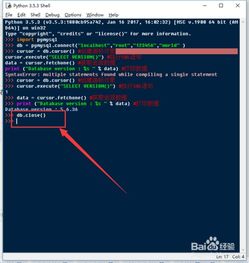
跟着Python3的遍及,越来越多的开发者开端运用Python3进行数据库操作。MySQL作为一款盛行的开源数据库,与Python3的结合运用也日益频繁。本文将具体介绍怎么运用Python3衔接MySQL数据库,包含装置必要的库、装备数据库衔接以及履行根本的数据库操作。
一、准备工作
在开端之前,请保证您的电脑上已装置以下软件:
Python3:能够从Python官方网站下载并装置。
MySQL:能够从MySQL官方网站下载并装置。
PyMySQL:Python衔接MySQL的库,用于树立数据库衔接。
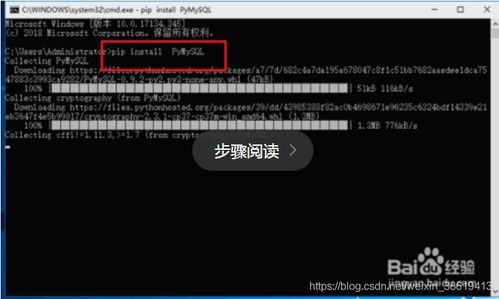
二、装置PyMySQL库
PyMySQL是Python衔接MySQL的库,能够经过pip指令进行装置。在指令行中输入以下指令:
pip3 install PyMySQL
装置完成后,您能够经过以下指令查看PyMySQL是否装置成功:
import pymysql
print(pymysql.__version__)
假如输出版本号,则表明PyMySQL已成功装置。
三、装备MySQL数据库
在衔接MySQL数据库之前,您需求保证MySQL数据库已装置并装备好。以下是装备MySQL数据库的过程:
翻开MySQL指令行东西。
输入以下指令创立一个新的数据库:
CREATE DATABASE test;
挑选该数据库:
USE test;
创立一个新用户并授权:
CREATE USER 'username'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON test. TO 'username'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
四、衔接MySQL数据库
在Python代码中,您能够运用以下代码衔接MySQL数据库:
import pymysql
数据库装备信息
config = {
'host': 'localhost',
'port': 3306,
'user': 'username',
'password': 'password',
'db': 'test',
'charset': 'utf8mb4',
'cursorclass': pymysql.cursors.DictCursor
树立数据库衔接
conn = pymysql.connect(config)
创立游标目标
cursor = conn.cursor()
履行SQL句子
cursor.execute(\
未经允许不得转载:全栈博客园 » python3衔接mysql,Python3衔接MySQL数据库的具体教程

 全栈博客园
全栈博客园 博看人文热销期刊数据库,博看人文热销期刊数据库——全面掩盖人文范畴的数字阅览渠道
博看人文热销期刊数据库,博看人文热销期刊数据库——全面掩盖人文范畴的数字阅览渠道 互联网大数据人工智能,未来开展的三大引擎
互联网大数据人工智能,未来开展的三大引擎 大数据对社会的影响,大数据的兴起与界说
大数据对社会的影响,大数据的兴起与界说 mysql二进制日志,功用、装备与运用场景
mysql二进制日志,功用、装备与运用场景 mysql乘法函数的运用方法,MySQL乘法函数的运用方法详解
mysql乘法函数的运用方法,MySQL乘法函数的运用方法详解








